
It doesn’t consider the subsistence farmers
I am unsure how this helps your argument.
If anything this all further reinforces the nature of unequal exchange and imperialism.
There are rarely any “true” full-time subsistence farmers in the Global South, for example, during periods of drought, or after seasonal harvests, - subsistance farming doesn’t guarantee full-time job security nor does it entail that (for example) the farmer is able to pay for school or healthcare for the farmer or their family.
and people who obtain resources without the market.
That is of statistical insignificance, unless you are going to argue that Capitalism and Imperialism (what you call the “market”) have not infilitrated atleast 5% of the world populace (400 million people). And if so - may I get a source? I must read about the 400 million people or more that escaped Capitalism!
Even if 80million people were not counted, 1% of the world population or the entire population of Germany, it would still not affect the conclusions made from the article and the map.
As described in the article:
To broaden the focus, we can apply the same reasoning, not only to the United States, but to the rich nations as a whole. We follow the World Bank’s classification of high-income countries:
The average national income per capita in high-income countries in 2021 is $55,225 per year (this and the following figures are in 2023 international dollars).
The total world population is 7.888 billion people.
Repaying the entire world’s population with the average income of the average citizen in high-income countries would require about $436 trillion per year.
However, the total national income of the entire world amounts to just $146 trillion annually.
If all the world’s annual income – eliminating the parasitic counterparts of labor: profit, rent, interest rates, etc. – was destined to simple reproduction, and thus distributed equally among the entire world population, it would be enough to cover barely one third of the average income of high-income countries: that is, about $18,510 per capita per year.
As long as the “proletariat” in the Global North earns more than their labour - earn more in return than their labour is entitled for - their material interests are in direct contradiction to the interests of the Global South masses.
Nor does it take into account cost of living.
It is using 2023 international dollars - so it does take into account cost of living, unless you are arguing that the World Bank’s “basket of goods” is flawed.
If you think about it, people who live “on less than a dollar per day” literally wouldn’t be able to live if they faced the same cost of living as people in western societies.
There is a difference between “living” and “surviving”.
The question we must ask ourselves is why is that? What makes their lives different from ours? What is considered essential, abundant or normal here that isn’t in the Global South?
To quote Unequal Exchange and the Prospects of Socialism by Communist Working Group and Arghiri Emmanuel.
The commodities which represent the reproduction costs of ther working class do more or less cost the same all over the world. generally speaking, the costs of maintaining a living as a Danish worker are the same in Denmark, Tanzania, Brazil or Hong Kong. The price for one kilo of wheat, one kilo of meat, one watch, or a transistor radio varies by 10, 20, 50 percent from country to country. However, the wages are 5, 10, 20 or 50, times higher in the imperialist countries.
Truthfully, that does not need to be quoted by I did anyways because the main point is that “living costs” is defined as the level needed for basic social reproduction. It does not entail short working hours, safe working conditions, the price of buying a meal at a restaurant, strong environmental regulations, the price of consumer goods or rent, etc.
The calculations in the main article explicitly mentions that it eliminated “the parasitic counterparts of labor: profit, rent, interest rates, etc.” by utilzing only data on production.
but the gap is exaggerated by the liberal worldview.
What is considered liberalism here?
It’s important to remember that a lot of this data is biased.
Yes but not necessarily for your own argument that the data is “exaggerated”.
The official data is given to the World Bank by member states, in which for Third World states, due to centuries of imperialist sabatoge, is unable to provide fully accurate statistics and often overrepresent organized workers. This means the disparity may even be larger in real life.
I recommend reading this article on the Labour Aristocracy and the book I quoted prior.
There has also been other extensive works on Imperialism in the late 20th and early 21st century that I think may help you understand the arguments being conveyed here.


See my comment above.
You are merely arguing against the presentation of the data on the map, not the methodology of the data or the conclusions made from the data.
PERCENTAGE OF THE NATIONAL POPULATION BELOW WORLD AVERAGE INCOME OR CONSUMPTION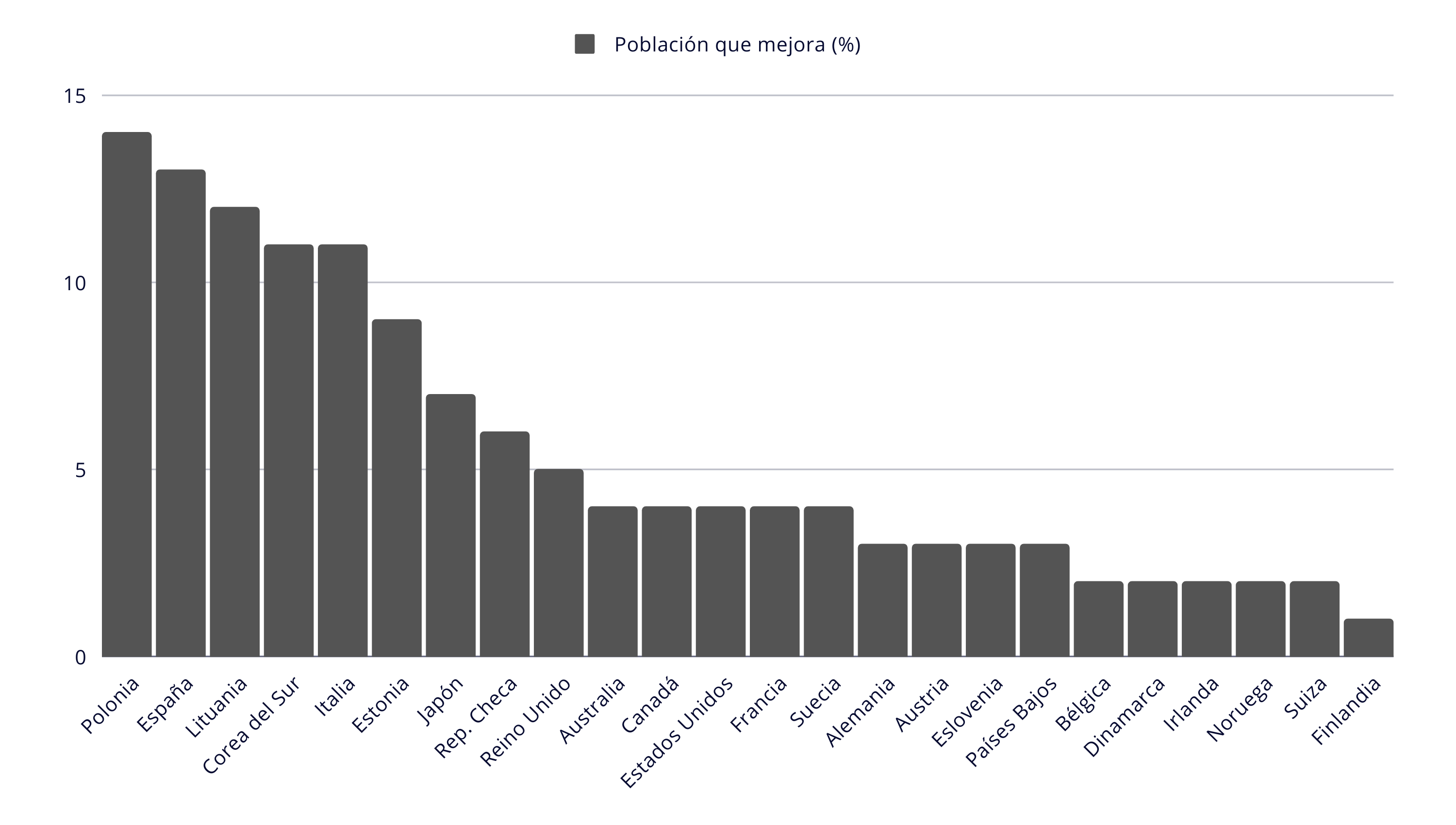
In this image found in the article I sourced the map from, it is made perfectly clear that Poland, with a population of 15% earning below the world average, is obviously vastly different than that of Switzerland of around 2%. In other words, proportionally, there are 7.5x more people in Poland that live with wages below the world average.
It is purely arbitrary that the author made the cutting off point for the legend 20%, when it could easily be in 10%, which would seperate Poland and Lithuania (but not Estonia) from Switzerland. The author could also have based it on quartile ranges (which would defeat the nature of this analysis).